FuncitonプロシージャのFunctionは関数です。
関数とは何でしたか。
y=f(x)です。
これは、引数xを渡すと、戻り値をyに戻す働きです。
Subプロシージャが戻り値をもたないのに対して、Functionプロシージャは戻り値をもちます。
簡単な例を作って、Functionプロシージャの働きを見てみましょう。
シート
コード
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim x As Integer, y As Integer
x = Cells(5, 2)
y = f(x)
Cells(6, 2) = y
End Sub
Function f(x As Integer)
f = 2 * x + 1
End Function
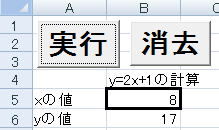
実行例

これはB5にxの値を入れると、2x+1を計算してその結果をB6に出力するマクロです。
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim x As Integer, y As Integer
x = Cells(5, 2)
y = f(x)
Cells(6, 2) = y
End Sub
簡単に、
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim x As Integer
x = Cells(5, 2)
Cells(6, 2) = f(x)
End Sub
としてもよいのです。
f = 2 * x + 1
によって、右辺が計算され、それがFunctionプロシージャfの値として、
呼び出された側に返されます。
では、このマクロを次のように改良しましょう。
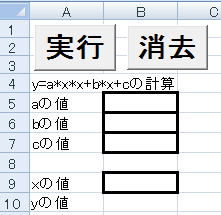
xの値だけでなく、各係数a,b,cも入力することが出来るように変更してください。
コード例は、30行下。
コード例
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim a As Integer, b As Integer, c As Integer, x As Integer
a = Cells(5, 2)
b = Cells(6, 2)
c = Cells(7, 2)
x = Cells(9, 2)
Cells(10, 2) = f(a, b, c, x)
End Sub
Function f(a As Integer, b As Integer, c As Integer, x As Integer)
f = a * x * x + b * x + c
End Function
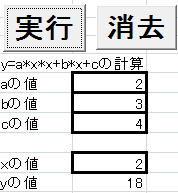
実行例
では、皆さんFunctionプロシージャを使って、『素数列挙マクロ』
シート
コード
Dim cn As Long
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim n As Long, i As Long
cn = 0
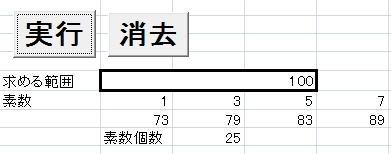
n = Cells(5, 2)
For i = 2 To n
f (i)
Next
Cells(7 + Int(cn / 20), 2) = "素数個数"
Cells(7 + Int(cn / 20), 3) = cn
End Sub
Sub f(n As Long)
Dim i As Long, r As Long
If n = 2 Then
Cells(6 + Int(cn / 20), 2 + (cn Mod 20)) = n
cn = cn + 1
Exit Sub
End If
If n Mod 2 = 0 Then
Exit Sub
End If
r = Sqr(n)
For i = 3 To r Step 2
If n Mod i = 0 Then
Exit Sub
End If
Next
Cells(6 + Int(cn / 20), 2 + (cn Mod 20)) = n
cn = cn + 1
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click()
Columns("B:U").Select
Selection.ClearContents
Cells(1, 1).Select
End Sub
実行画面例
を書き直してみましょう。
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click側は、
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim cn As Long
Dim n As Long, i As Long
cn = 0
n = Cells(5, 2)
For i = 2 To n
If f(i) = 1 Then
Cells(6 + Int(cn / 20), 2 + (cn Mod 20)) = i
cn = cn + 1
End If
Next
Cells(7 + Int(cn / 20), 2) = "素数個数"
Cells(7 + Int(cn / 20), 3) = cn
End Sub
とさせていただきます。このマクロのよい点は、グローバル変数を用いていない点です。
ローカル変数は、プロシージャが終わると、プロシージャもプロシージャ内の変数も消滅し、メモリが解放されます。
それに対して、グローバル変数はプログラムの実行中メモリに常駐することになり、メモリの無駄遣いになります。
ですから、メモリの節約のためにはなるべくグローバル変数は使用しない方がよいわけです。
では、皆さんFunction f(n As Long)側を考えてください。
第5講第7話へ 第2話へ
